The 3D printing industry is one of the fasters growing industries in the globe. One of the reasons why the industry keeps growing so fast is that applications of this technology keep increasing by the day. It is, therefore, a fact that 3D technology has led to a new era in more than a couple of sectors. There are several types of 3D printing machines in the market used for a variety of applications. FDM 3D printers are the most popular forms of 3D printers in the aspect. One of the reasons for its popularity is the quality of the Extruder Calibration. In this post, we discuss the concept of FDM 3D printers in and out.
What is an FDM 3D printer?
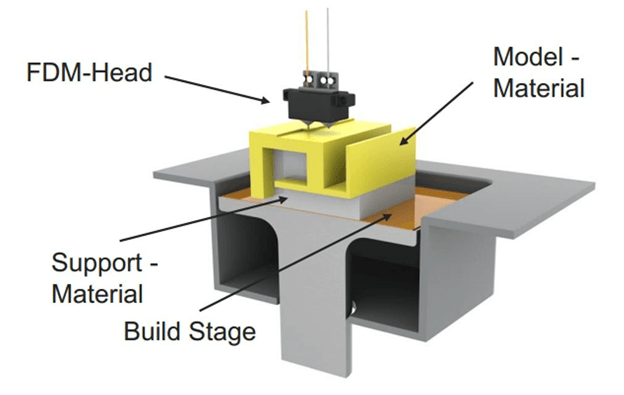
The term FDM is an acronym for Fused Deposition Modelling. Like other forms of 3D printing, it is a mode of additive manufacturing and a member of the family of material extrusion. Also known as Fused Filament Fabrication, FDM 3D printing manufactures products through selective deposition of raw material in molten form. FDM 3D printers deposit the molten layer by layer using a path that is previously determined according to the design and nature of the end product. In addition to being the most commonly employed type of 3D printer, it is also one of the oldest technologies developed in 3D printing.

How do FDM 3D printers work?
The following steps provide a breakdown of how FDM 3D printing technology works;
- Loading of the printer
This step is where the printer is loaded with the thermoplastic filament. Before the filament is loaded into the printer, the nozzle is exposed to high temperatures. The temperature is set depending on the material and the desired end product. The filament is fed into the printer in solid form. The heat in the nozzle facilitates the transformation of the thread into a molten state. The material is fed into the printer through the extrusion head.
- Extrusion of the filament in molten form
Once the filament is melted, it goes through an extrusion process. The molten filament is extruded in tiny strands that are deposited in a predetermined location. The location is influenced by design shape that if fed to the printer before the process begins. The extrusion is done through an extrusion head which is attached to three axes. The X, Y, and Z-axis move in different process as the material is deposited one layer after another.
- Cooling
Once the material is deposited, it is left to cool down and solidify. But, to allow this process, the extrusion head is moved upwards, and the platform is pushed down. Tampering with the equipment before it cools down would affect the integrity of the final product. The cooling process is accelerated using fans that are attached to the extrusion head.
Take Away
The material used in 3D printing usually features a melting point of two hundred and fifty degrees or less. The higher the melting point, the higher the cost of production. Also, a virtual model has to be fed to the printer for it to produce a physical model.